Bitcoin, the pioneer of decentralized digital currencies, has been celebrated as the epitome of financial privacy and autonomy.
Originally touted as a currency that provides unparalleled anonymity, the reality isn’t so straightforward.
While it offers enhanced privacy features compared to traditional banking systems, the degree to which Bitcoin transactions are traceable is a topic of contention.
In this article, we will delve into various aspects that determine the traceability of Bitcoin transactions and try to explain why bitcoin transactions are pseudonymous.
Understanding the Basics: How Does Bitcoin Work?
Before we discuss traceability, it’s essential to understand how Bitcoin transactions work.
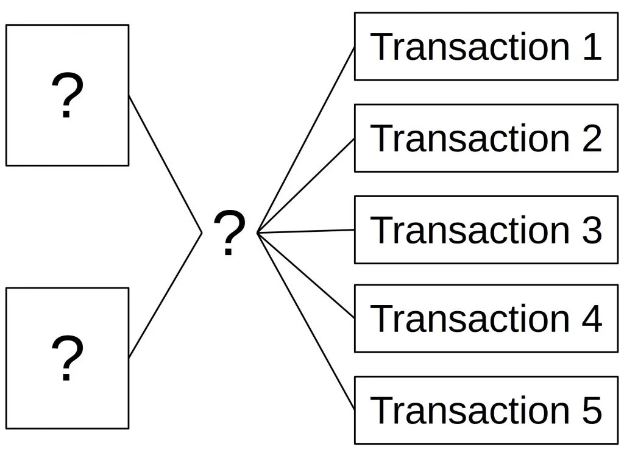
The Bitcoin network operates on a public ledger known as the blockchain. Transactions between parties are recorded in ‘blocks’ on this chain. Importantly, all these transactions are transparent and publicly accessible, albeit pseudonymous—meaning, they are not directly linked to individuals but rather to digital addresses.
Pseudonymity Vs Anonymity: The Nuanced Differences
Many people often interchangeably use the terms “pseudonymous” and “anonymous,” but they’re not identical.
Anonymity means the absence of any identifying feature; pseudonymity implies the presence of a public identity (like a Bitcoin address), even though this cannot be easily linked back to an individual.
While traditional bank accounts are directly tied to individuals or entities through personal information, Bitcoin addresses do not inherently carry such identifications.

What Could Make Bitcoin Less Anonymous?
1. Exchange Regulations:
Governments and international organizations could implement stronger regulations that require cryptocurrency exchanges to perform rigorous Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) checks.
With stronger compliance measures, these platforms would collect and maintain more extensive user information, potentially sharing it with law enforcement agencies if required. This could make it easier to link Bitcoin wallet addresses to real-world identities.
2. IP Addresses:
If you’re not careful with your online footprint, your IP address could reveal your identity.
3. Third-Party Tools:
As chain analysis software continues to evolve, the ability to track transactions and link them to real-world identities could improve.
These tools are getting better at clustering transactions to identify ownership patterns, conducting taint analysis to trace illicit transactions, and even correlating blockchain activity with other data points like IP addresses and social media posts.
4. Improved Chain Analysis Tools
If people become more informed about how Bitcoin transactions work, they may be less likely to take necessary precautions to preserve their anonymity.
Careless behaviors—such as reusing addresses or using the same address for both legal and illegal activities—can make it easier to link identities to transactions.
Chain Analysis and Traceability: How Advanced Tools Can Unmask Identities
Blockchain analytics companies like Chainalysis, Elliptic, and CipherTrace specialize in tracing cryptocurrency transactions. Their advanced algorithms and tools can de-anonymize the blockchain to some extent by:
1. Cluster Analysis:
There are several methodologies employed by chain analysis tools. One common method is ‘clustering,’ which combines addresses controlled by the same entity based on their transaction behavior.
For instance, when multiple inputs are used in a single transaction, it’s a strong indicator that those inputs belong to the same user.
Over time, by analyzing transactions that involve large and complex clusters of addresses, one can draw increasingly accurate inferences about the identity of the entity or entities controlling them.
2. Taint Analysis:
Another methodology is ‘taint analysis.’ This technique traces the flow of ‘tainted’ coins that were involved in illicit activities.
The idea is to follow the path of these coins as they are split, combined, and transferred, potentially identifying the wallets involved in money laundering or other illegal operations.
This kind of traceability is critical for law enforcement agencies that are tracking criminal activities.
Timing analysis and social network analysis are other advanced methods.
Timing analysis looks at the timing between different transactions to make educated guesses about their connection.
Social network analysis goes beyond the blockchain data to correlate transactions with social media activity, forum posts, or data leaks, providing a more comprehensive view of an entity’s behavior.
However, it’s worth mentioning that advanced users employ various obfuscation techniques to counter chain analysis.
Mixing services, CoinJoin transactions, and even switching between different cryptocurrencies are common methods used to obscure transaction trails.
Nevertheless, advanced chain analysis tools are continually evolving and adapting to these tactics.
The Role of Mixing Services: Do They Provide Anonymity?
Some Bitcoin users turn to mixing services (or tumblers) to enhance anonymity. These services take a group of transactions and mix them, redistributing the mixed coins back to the original owners. The idea is to muddy the waters and make tracing more challenging.
However, using a mixing service itself can raise red flags and invite scrutiny. Moreover, the efficacy of these services is not foolproof.
Real-Life Instances: Bitcoin Traceability in Legal Cases
Law enforcement agencies have successfully traced Bitcoin transactions in high-profile cases, debunking the idea of complete anonymity.
The takedown of online marketplaces like Silk Road is a testament to Bitcoin’s traceability.
Ross Ulbricht, the founder, was caught partly because of his traceable financial transactions on the Bitcoin network.
Enhancements and Future Developments: Moving Towards More Privacy?
Technological advancements like the implementation of the Lightning Network, CoinJoin, and other privacy-preserving techniques are in the pipeline or already operational.
However, they offer a trade-off between anonymity and other features like transaction speed or cost.
Concluding Thoughts: So, Is Bitcoin Fully Traceable?
Bitcoin exists in a grey area when it comes to traceability. While it offers more privacy compared to conventional financial systems, calling it entirely anonymous would be misleading.
Traceability is conditional and depends on various factors, including how one uses Bitcoin and advances in blockchain analytics.
Therefore, if complete anonymity is crucial, one must take extra steps to obscure their identity and be aware of the potential limitations and risks involved.
As technology advances, so do the tools for both maintaining privacy and breaking it. Thus, the question of Bitcoin’s traceability is a dynamic one and likely to evolve in the coming years.